Managing Networks
- Network Manager is available for Firewalla Gold, Purple, and Orange series boxes. It is used to configure the WAN in Router Mode and also create network segments in both Router and Simple/DHCP Modes. If you are in Bridge Mode, it can help you manage your network bridges.
- Network Manager is accessible even if your network is down; You just need to stand closer to the physical unit.
- Firewalla supports multiple WANs; this is configured via the network manager.
- Network Manager is also used to provision VLANs or port-level network segmentation.
To configure any network functions, you will need to press the Edit button
Default Networks
By default, there are two networks on Firewalla Gold/Purple/Orange:
- A WAN connection you configured during the initial setup, if Firewalla is in Router Mode.
- A default Local Network (LAN) that bridges the rest of the Ethernet Ports. Devices can join Firewalla's default Local network by connecting directly to one of these ports using an Ethernet cable, or to a wireless access point or wired switch that connects to these ports.
Firewalla Gold has 4 Ethernet ports. Port 4 is the default WAN port in Router Mode, and the default port connects to the router in Simple/DHCP Mode. Ports 1, 2, 3, and 4 can be configured to have their own network space. They can also be configured as VLAN trunking ports.
Here is a guide on how to change the default port 4 used for the WAN connection into another port.
Firewalla Purple and Firewalla Orange have 2 Ethernet ports; the WAN port is the default WAN port in router mode, and the LAN port is the default port that connects to the router in Simple/DHCP mode.
Network Manager
The Network Manager screen (Home -> Network) shows all the existing networks with their IP range, VLAN ID, and the Ethernet ports they are using.
If you want to create your own network, tap Create Network, then choose the network type.
Wi-Fi Local Networks
- If you are using Firewalla Purple or Firewalla Orange, you'll find more options for Wi-Fi networks. To learn more about how to manage Wi-Fi Local Networks, see our articles on:
- If you are using Firewalla Gold and you have the Wi-Fi SD dongle, see our article on Wi-Fi SD for Firewalla Gold.
- If you are using Firewalla Access Point 7, you'll be able to customize multiple SSIDs to fit your network. To learn more about AP7 Wi-Fi, see our article on Getting Started with Firewalla Access Point 7.
WAN Connections
During the initial setup, Firewalla will auto-detect the connection type of your network. In case the auto-detection fails, you can also set up your WAN connection manually by tapping Manual Setup.
If you wish to have more than one WAN connection, you can create a new connection in Network Manager after the initial setup. Please find more details here: Firewalla feature guide: Multi-WAN.
Basic Settings
To create a WAN connection, you'll need to select an Ethernet port connected to your ISP device (a modem or router) and then enter a VLAN ID (if any) and a connection type.
There are 4 types of WAN connections when you set up a new WAN:
- DHCP: Get the IP Address assigned by the modem/router automatically.
-
Static IP: Manually assign an IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, and DNS server for your connection. The static IP should be provided by your ISP. Otherwise, please make sure the IP Address is in the subnet of the router you are connected to.
For those of you who are given multiple static IP addresses by your ISP, Firewalla supports configuring additional IP addresses on your WAN connection. By assigning multiple IPs on a single WAN, you can forward different ports to different IP addresses and set the DMZ host on any specific IP address. Find more details here. - PPPoE: This requires an ISP-provided username and password to connect to the Internet.
- Triple Play: Choose this type only if it is required by your ISP.
You can also edit an existing WAN if your needs change after you created it.
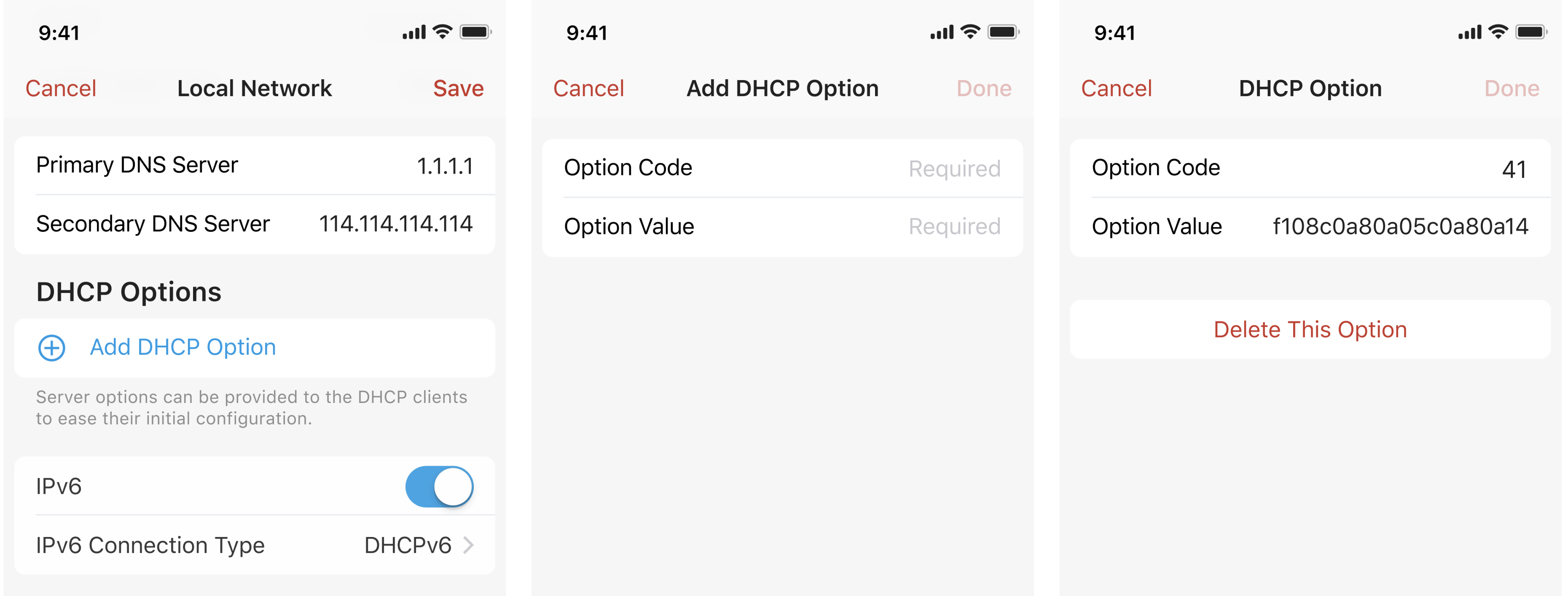
DHCP Options
When connecting to the Firewalla box, some devices may require certain DHCP options to function normally. In this release, we've provided a flexible way of configuring DHCP options on both WAN (client options) and LAN (server options) networks. Below DHCP options are supported now.
| WAN | 12, 43, 51, 60,61 |
| LAN | 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 26, 27, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 40, 41, 42, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 58, 59, 60, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 74, 77, 80, 93, 94, 97, 119, 120, 121, 125, 150, 255 |
For example, if you want to set up DHCP option 41 on Firewalla for your AP devices, you can tap a LAN network on the Network Manager page, scroll down to find the DHCP Options, tap add DHCP option, and configure the option code and value accordingly.
Advanced Settings
In addition to the basic settings, we've added some advanced options in case your ISP requires additional configurations when creating a WAN connection:
- Supports VLAN ID
- WAN DNS Servers, including IPv4 and IPv6 (requires App 1.67 or later)
- Change/Clone MAC Address of Ethernet Ports
- IPv6 Support: Addresses, Prefixes, and DNS Servers
- DHCPv6 Support: Lease Info and DUID Type (if your ISP doesn't require a specific type, there is no need to change this value)
- Multiple WAN IP Addresses for Static IPs
- IGMP Proxy - Often used with IPTV, which uses multicast traffic
- MTU for all WAN types and MRU for PPPoE (The default MTU value for PPPoE is 1492, and the default value for Static IP and DHCP is 1500. If your ISP hasn't given you any specific requirements for MTU, there is no need to change this value.)
- Connectivity Test settings
- Block ICMP (Ping)
You can configure the connectivity test target for each WAN connection. The tests will be used to monitor the Internet connectivity of the WAN connections, send you network events when your network goes down, and failover to the standby WAN if you have multiple WANs. Learn more about network events.
IPv6 Support
You can turn IPv6 on or off. If you have IPv6 enabled, you can turn IA_NA on or off. IA_NA allows Firewalla to obtain an IPv6 address from your ISP. Some ISPs need this feature to be disabled.
You can request multiple IPv6 prefixes under Advanced Settings -> IPv6 Prefix. For those ISPs (e.g., AT&T Fiber) that provide multiple /64 prefixes instead of a single prefix with a larger subnet capacity, increasing the number of IPv6 prefixes allows you to receive multiple IPv6 prefixes, enabling full IPv6 support across multiple VLANs.
You can also set primary and secondary DNS Servers for IPv6 (requires App 1.67 or later).
DHCPv6 Support
Additionally, you can see information about each WAN's DHCPv6 lease, including the DHCPv6 server, lease lifetime, and IPv6 prefix lifetime. We've also added an option to manually renew the DHCPv6 Lease.
Some ISPs require a specific DHCPv6 DUID type, and the default may not always be compatible. For each WAN connection, you can select the DUID type as DUID-LLT, DUID-LL, or DUID-UUID. Note that unless your ISP requires a specific type, there is usually no need to change this value.
Multiple WAN IP Addresses
Firewalla supports configuring additional IP addresses to your WAN connection if your ISP has given you more than one IP address. If you assign multiple IPs to a single WAN, you can forward different ports to different IPs and set the DMZ host on any specific IP address.
Up to 12 additional IPs are supported on one WAN interface.
Local Networks
Basic Settings
To create a local network, you'll need to enter:
- A VLAN ID. Only if you are creating a virtual network.
- Ethernet port(s). If you select more than one port, they will be bridged automatically.
- Network settings. Firewalla fills the network settings for you. You can tap the blue "Suprise Me" button to generate a new one, or manually edit them as per your preference.
After the network is created, you can connect your devices to the ports with Ethernet cables, or through a wireless access point or a router that has been set to Bridge Mode/ AP Mode. Learn more about how to connect your devices.
Note: if you create a VLAN on a Firewalla port and connect a device to that port, the port will become tagged. This means you must configure the device with the correct VLAN ID in order for it to properly connect to the VLAN.
Advanced Settings
DNS Servers
Firewalla will automatically become the default upstream DNS for the entire LAN. So in this case, only Firewalla itself will use WAN-configured DNS. Note that if DNS over HTTPS (DoH) is enabled on Firewalla, the devices it's applied to will use the DoH server. If multiple servers are enabled in DoH, Firewalla will go with the server with the lowest latency.
You can specify specific DNS Servers for IPv4 and IPv6 (requires App 1.67 or later).
Search Domain
By default, Firewalla uses .lan for all local networks. You can set different search domains for different local networks as needed.
DHCP Options
Some devices may need special DHCP options. We've provided a flexible way of configuring DHCP options on both WAN (client options) and LAN (server options) networks. Below DHCP options are supported now.
For example, if you want to set up DHCP option 41 on Firewalla for your AP devices, you can tap a LAN network on the Network Manager page, scroll down to find the DHCP Options, tap add DHCP option, and configure the option code and value accordingly.

IPv6 Delegation
If you have multiple IPv6 WANs and want a certain LAN's IPv6 address to be delegated by a specific WAN, scroll down in your LAN's network settings to locate IPv6 Delegation, switch to Manual, and select a WAN with DHCPv6 enabled. Check out our video tutorial for detailed instructions.
mDNS Relay and SSDP Relay
mDNS Relay and SSDP Relay are different protocols that allow some devices (such as Sonos speakers or Roku) to discover each other across networks.
For example, if you have a smart speaker on LAN 1 and you want it to be discoverable by your phone on different networks, you can enable SSDP and mDNS Replay on LAN 1. It's possible that, in some cases, the app (like your phone) initiates the connection, not necessarily the device (such as the smart speaker). To make sure the phone can communicate with the device on a different LAN, you could also enable SSDP and mDNS Relay on the network to which the phone is connected.
To enable one or both of them, tap on a LAN, tap Edit, and then toggle mDNS Relay and/or SSDP Relay on.
- If SSDP Relay is enabled on one network, SSDP broadcast queries sent from the network will be relayed to all the other networks.
- SSDP is a discovery protocol; once devices find each other, they can communicate without an SSDP Relay. To make sure devices in different networks stop talking to each other, we recommend you reboot the device or reconnect it to your network after turning off SSDP Relay.
- SSDP Relay is only supported in Router Mode on all local networks.
- SSDP Relay is not supported on VPN networks (OpenVPN and WireGuard)
Note that mDNS Relay was previously called mDNS Reflector and was located on the Configurations page. mDNS Relay is the exact same feature as mDNS Reflector; it's just been moved.
NAT Settings
To provide better control of NAT functionality in Firewalla, we have consolidated all NAT functions under Network -> NAT Settings. If you do not have advanced networks, there is no need to modify this.
- Source NAT (default on)
- Source Networks
- Source NAT Rules/1:1 NAT
- NAT Passthrough
- Port Forwarding
- DMZ
Source NAT (default on)
If Source NAT is turned on, it means the local networks can access the Internet through the SNAT gateway. If you have multiple WANs, Source NAT can be turned on/off on each WAN connection separately, but all WANs will share the same list of source networks. Note that there is no need to configure this in most networks.
Source Networks
Source NAT is turned on for all local networks by default. In addition, you can manually add source networks.
Source NAT Rules/1:1 NAT
If your Internet Service Provider has given you several IP addresses, you might want to assign a particular outgoing WAN IP address for specific devices, groups, users, networks, or all devices.
To do this, tap Source NAT Rules > Add Source NAT Rule > select a device and a WAN IP address > tap Save to apply the changes. Check out our video tutorial for step-by-step instructions on how to use this feature.
Note that this type of rule is only available for WAN connections with Static IP addresses.
NAT Passthrough
NAT Passthrough helps connect protocols to pass through the router, including:
- PPTP
- L2TP
- IPSEC(for VPN and Verizon WiFi Calling)
- H323 (for video call)
- SIP (for VoIP)
If you have a VPN set up on your device and are having trouble getting it to work, you may need to enable one of these options (depending on the VPN protocol).
If you are not having any problems, please keep these buttons off.
Port Forwarding
UPnP per network
For users who only want to enable UPnP for specific networks, say a gaming VLAN, you can configure it on your local networks separately.
- In Network Manager, go to NAT Settings > Port Forwardings, tap Apply To > Specific Networks, and you can check/uncheck your networks.
(Please note there is a known issue that the UPnP ports will be hidden 30 mins after expiration or disabling, so you may not see an immediate change after turning off UPnP on your networks, even though the ports are already closed, and UPnP is disabled. This issue will be fixed in the upcoming release. )
For each port forwarding, you can:
- Choose a protocol (TCP or UDP).
- Specify an external port, and optionally a WAN or VPN – note that doing this only allows one port forwarding for each external port per WAN IP, and AnyConnect VPNs are not supported as of box version 1.975. To learn more, see our video tutorial.
- Specify an internal port on a specific device.
- Choose whether to create an allow rule for open ports – this allow rule will be applied to the corresponding device.
You can block any port forwarding created by UPnP and delete any manually created port forwarding.
Here are our tutorials on how to create port forwarding and limit access on ports:
DMZ
Select one device as a DMZ Host so that it can be accessed directly from the outside of your network.
- In Network Manager, go to NAT Settings > DMZ > Enable DMZ
- Specify one device or IP address as the host > Tap Save.
If Allow is set to All Sources, an allow rule will be created on the device to allow all traffic from the internet as well. You can choose to allow only specific internet traffic to access your DMZ host using Target Lists, IP addresses/ranges, or regions.
Example
Comments
10 comments
With IPv6 enabled, is it possible to override the ISP-assigned IPv6 DNS servers and use your own preferred ones, such as Cloudflare (2606:4700:4700::1111 and 2606:4700:4700::1001)?
Basically I would prefer to have the router push these out via DHCP rather than have to manually configure them on each device.
Also, does the DNS over HTTPS work with IPv6 DNS AAAA records?
+1 for this as well. Also, how can a custom Prefix Delegation be set?
I just ran into the same issue.
To fix this for android, windows 10, etc here is what I did.
You ssh into the firewalla gold and make a new file in /home/pi/.router/config/dhcp/conf/
For example:
nano /home/pi/.router/config/dhcp/conf/gero.conf/custom_v6_dns.conf
In the file you put
dhcp-range=tag:br0,::,constructor:br0,slaac,ra-stateless,86400
dhcp-option=tag:br0,option6:dns-server,[fd68:a4d3:aaf6:20::53]
but replace the ip with your own ipv6 dns server and br0 with what you use (run "ip add" to check).
Then reboot the firewalla
sudo reboot
Then disabled/enabled network on windows 10 and it populated the ipv6 dns
You can now see the dhcpv6 responses with the dns server by running
sudo tcpdump -i br0 -n -vv '(udp port 546 or 547) or icmp6'
for example
I had a problem with SIP calls and enabling SIP under the NAT Passthrough option solved it. Can you please explain what exactly does this option do in a technical sense? Thanks.
This article should explain the ALG part https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Application-level_gateway
Ok, so enabling NAT Passthrough activates ALG for those services.... why isn't it on by default? Does it consume resources when turned on? Or is there a security aspect to it?
What format is the MAC address supposed to be in? No matter what I try, xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx, xxxxxxxxxxxx, it says "invalid MAC address" even though it's the one copied from the router.
@Dave try this format aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff
Ah, thanks. And a request for the Firewalla folks, could fields for entering MAC addresses be made a bit more flexible? The xx-xx form is standard for MAC addresses with the hex-digits-one probably being the next most common, without @Michael's hint I'd never have guessed that colons are required. So for validation, take the input, remove any punctuation, and then check that it's 12 hex digits, that allows xx-xx, xx:xx, and xxxx forms.
Do you have any insights about how to use more than 5 WAN IPs?
I’m looking to use firewalla in a SOHO environment but the 5 IPs per WAN is a big issue here…
Please sign in to leave a comment.